
Raum: PB-A 107
 +49 271 740-2174
+49 271 740-2174
 heck@bau.uni-siegen.de
heck@bau.uni-siegen.de
Effect of fibre distribution and fibre orientation on the residual flexural tensile strength of ultra-high performance fibre reinforced concrete (UHPFRC)
Research topic
Design and construction with ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC)
Funding and project duration
German Committee for Structural Concrete (Deutscher Ausschuss für Stahlbeton, DAfStb), Research Project V 501, sub-project A
Duration: January 2019 until October 2020
Person in charge
Lennart Heck, M.Sc.
Project description
The objective of the research project was to validate the results and findings obtained in the context of DAfStb Research Project V 497 by means of additional opto-analytical investigations of the specimens. Thus, the intended regulations of the DAfStb Guideline "Ultra-High-Performance Concrete" for the conversion between residual flexural tensile strength and axial post-cracking tensile strength should be checked und confirmed.
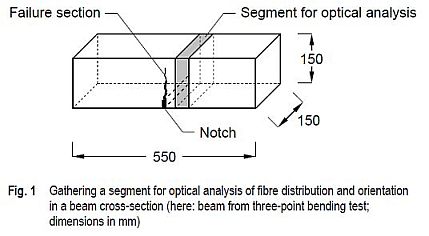
The examination of fibre distribution and orientation was performed on 54 beams (9 series of 6 beams each). The beams were fabricated with various maximum aggregate size, fibre geometry, and fibre volume fraction and have been tested in three-point or four-point bending tests within the scope of the DAfStb Research Project V 497. An approx. 4 cm thick segment was sawn out of the undamaged area of the beams near the cross-section where the bending failure had occurred (Fig. 1). The side facing the fractured cross-section was polished to reconstruct the elliptical shape of the cut fibres. Thereafter, high-contrast and high-resolution photographs of the polished surface were taken.
The opto-analytical evaluation of the fibre distribution and orientation was carried out by means of the FiDiOr analysis software. Based on these data, the mean fibre orientation coefficient of the volume and the "effective" fibre volume fraction were calculated for each analysed cross-sectional area (or parts thereof).
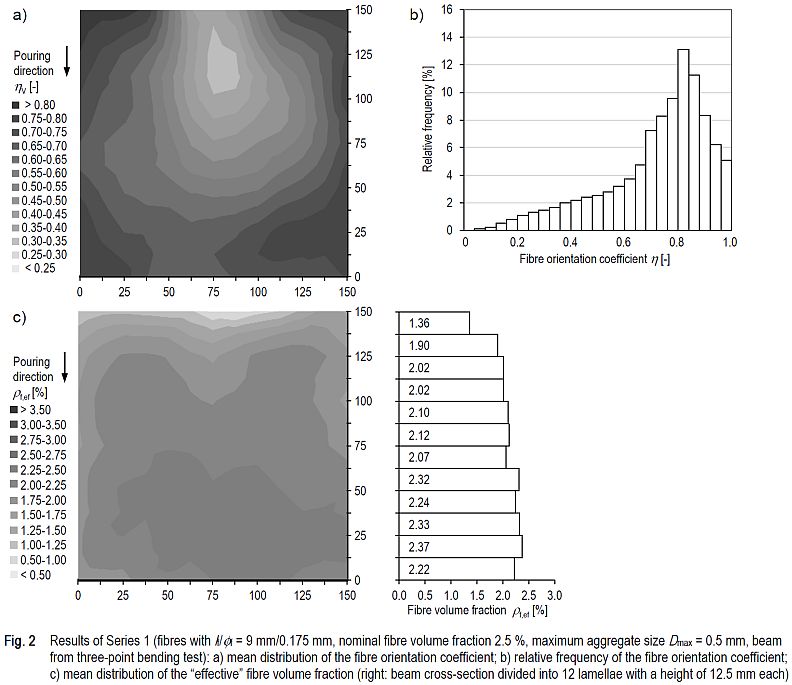
Mean fibre orientation coefficients in the beam cross-sections of 0.54 to 0.67 indicate that the fibres are preferably oriented in the flow direction of the fresh concrete, i.e. in the direction of the longitudinal axis of the beam, when pouring the concrete from one front end of the beam formwork. The orientation in the longitudinal direction of the beam is more pronounced with long fibres and small maximum aggregate size than with short fibres in coarse-grained UHPFRC. The load-bearing capacity determined in bending tests (DAfStb Research Project V 497) correlates with the fibre volume fraction active in tensile direction in the beam cross-section (= product of fibre orientation coefficient and "effective" fibre volume fraction). However, the load-bearing capacity only increases less than proportional with increasing active fibre volume fraction.
For most UHPFRC mixtures, a slight increase in fibre volume fraction towards the bottom surface of the cross-section can be observed (Fig. 2c). A systematic influence of fibre length, maximum aggregate size or nominal fibre volume fraction cannot be detected. With regard to fibre orientation, a systematic heterogeneous distribution within the beam cross-section is evident for all series (Fig. 2a). Fibre orientation coefficients of less than 0.5 in the middle third of the upper half of the cross-section indicate that the fibre orientation deviates significantly from the longitudinal axis of the beam. The reason for this is assumed to be turbulent flow of fresh concrete while filling the mould.
Direct tensile tests on specimens sawn out of beams (DAfStb Research Project V 497) indicate that the systematic heterogeneous distribution of the active fibre volume fraction correlates with a systematic heterogeneous distribution of the axial post-cracking tensile strength within a beam cross-section. By notching and rotating the beam by 90°, however, the effects of the systematically heterogeneous distribution of the active fibre volume fraction are largely compensated.
Theoretical considerations show that, compared to a homogeneous distribution of the active fibre volume fraction, the three-point bending test yields slightly lower load-bearing capacities, whereas the (un-notched) beams tested in four-point bending tests tend to yield slightly higher load-bearing capacities due to the systematic heterogeneous distribution of the active fibre volume fraction. However, a significant influence of the systematic heterogeneous distribution of the active fibre volume fraction on the relationship between axial post-cracking tensile strength and residual flexural tensile strength can virtually be excluded.
Publications
LEUTBECHER, T., 2022. Influence of fiber orientation on the mechanical properties of ultra-high performance fiber-reinforced concrete | Einfluss der Faserorientierung auf die mechanischen Eigenschaften von ultrahochfestem Stahlfaserbeton. In: Kongressunterlagen 66. BetonTage: Nachhaltiger Bauen mit Beton. Ulm, 21.-23. Juni 2022. Betonwerk und Fertigteil-Technik/Concrete Plant and Precast Technology. 88(6), 72. ISSN 0373-4331
