.jpg)
Univ.-Prof. Dr.-Ing. Torsten Leutbecher
Raum: PB-A 111/2
 +49 271 740-2592
+49 271 740-2592
 leutbecher@bau.uni-siegen.de
leutbecher@bau.uni-siegen.de
Effect of fibre orientation on the compressive strength of ultra-high performance fibre reinforced concrete (UHPFRC)
Research topic
Design and construction with ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC)
Funding and project duration
German Committee for Structural Concrete (Deutscher Ausschuss für Stahlbeton, DAfStb), Research Project V 501, sub-project B
Duration: January 2019 until October 2020
Person in charge
Philipp Riedel, M.Sc.
Project description
Depending on the geometry and casting method, structural members made of fibre reinforced concrete may (locally) show very different fibre orientation. As a result, the fibre reinforced concrete no longer behaves isotropically, but shows different tensile and compressive behaviour depending on the direction of loading. This aspect is of special importance for ultra-high performance concrete (UHPFRC), since UHPFRC is typically applied with high fibre volume fraction. Up to now, there was a lack of meaningful data in order to be able to quantify the anisotropy in compression caused by the fibres.
Thus, the influence of fibre orientation and fibre volume fraction on the failure pattern and on the compressive strength of fine- and coarse-grained UHPFRC was extensively investigated in a series of tests. The experimental programme consisted of five series of compression tests on cylinders with h/d = 200 mm/100 mm and cubes with d = 100 mm made of UHPFRC. The study focused on UHPFRC mixtures with fibre volume fractions between 1.5 % (fibre with large aspect ratio) and 3.5 % (fibre with small aspect ratio). Further, the nominal maximum size of coarse aggregate Dmax and the fibre length lf were varied within the range of practical application.
For each series, 9 cylinders (Cyl) and 12 cubes (Cube A) were cast in standard molds as well as three beams with l/b/h = 750 mm/100 mm/100 mm (Fig. 1, left). The beam molds were filled from one end of the formwork in order to provoke a predominantly unidirectional orientation of the fibers parallel to the longitudinal axis of the beam. Four cubes with an edge length of about d = 100 mm were sawn out of the center of each beam, so that another 12 cubes (Cube B) per series were provided for the compressive strength tests.
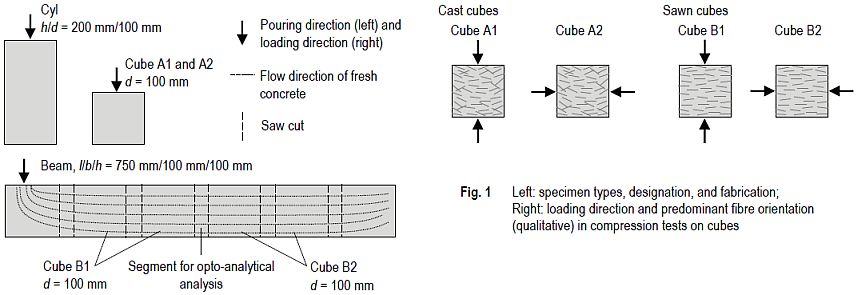
The cylinders as well as 6 of the cubes (Cube A1) fabricated in standard molds and 6 of the cubes (Cube B1) sawn out of the beams were loaded in casting direction. The remaining cubes (Cube A2 and Cube B2) were tested perpendicular to the direction of casting. Fig. 1, right, shows the direction of loading for the four groups of cubes, qualitatively illustrating the orientation of fibers.
For all series, the exact fibre orientation was determined at different sections of the specimens by an opto-analytical method. Furthermore, a non-destructive induction method was applied for determining the fibre volume fraction and the mean proportional fibre alignment with regard to the three spatial directions.
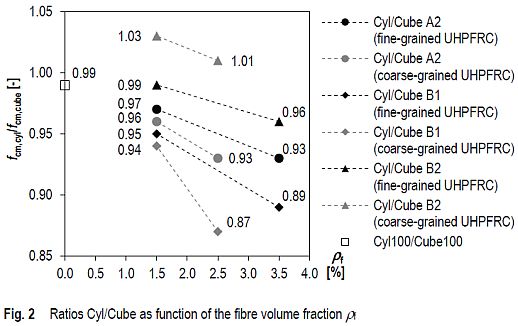
The results show that with predominantly unidirectional alignment of fibres in the plane perpendicular to the loading direction, the compressive strength increases significantly with increasing fibre volume fraction. In contrast, the influence of fibre volume fraction is marginal with predominantly unidirectional alignment of fibres in the direction of loading. Depending on the loading direction, the compressive strength tested on cubes differs by up to 26 MPa and 14 %, respectively. The difference between cube and cylinder compressive strength increases with increasing fibre volume fraction (Fig. 2). For instance, the difference of compressive strength of cylinders and cubes fabricated in standard moulds is approximately 5 to 7 MPa with a fibre volume fraction of 1.5 % and 11 to 13 MPa with a fibre volume fraction of 2.5 to 3.5 %.
To be conservative in material testing, the authors suggest to compute the cylinder compressive strength by the equation fck,cyl = fck,cube - 15 MPa in cases where the compressive strength of UHPFRC is tested on cubes. Alternatively, the influence of fibre volume fraction may be considered in a more refined way. Based on the suggested simplified conversion, the concrete strength classes result in C130/145, C150/165 and C175/190.
Based on the present study, a particular reduction of cylinder compressive strength seems not necessary to account for an "unfavourable" fibre orientation in structural members.
Publications
LEUTBECHER, T., 2022. Influence of fiber orientation on the mechanical properties of ultra-high performance fiber-reinforced concrete | Einfluss der Faserorientierung auf die mechanischen Eigenschaften von ultrahochfestem Stahlfaserbeton. In: Kongressunterlagen 66. BetonTage: Nachhaltiger Bauen mit Beton. Ulm, 21.-23. Juni 2022. Betonwerk und Fertigteil-Technik/Concrete Plant and Precast Technology. 88(6), 72. ISSN 0373-4331
LEUTBECHER, T.; RIEDEL, P., 2022. Einfluss der Faserorientierung auf die Druckfestigkeit von stahlfaserbewehrtem UHFB. In: BERGER, J., Hrsg. Innsbrucker Bautage 2022: Festschrift zum 60. Geburtstag von Univ.-Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jürgen Feix. Innsbruck: STUDIA Universitätsverlag, S. 287-298. Innsbruck - Massivbau und Brückenbau, Band 7. ISBN 978-3-99105-024-7
RIEDEL, P.; LEUTBECHER, T., 2021. Effect of Fiber Orientation on Compressive Strength of Ultra-High-Performance Fiber-Reinforced Concrete. ACI Materials Journal. 118(2), 199-209. ISSN 0889-325X. doi:10.14359/51730417
RIEDEL, P.; LEUTBECHER, T., 2020. Einfluss der Faserorientierung und des Fasergehalts auf die Druckfestigkeit von ultrahochfestem Beton. Beton‐ und Stahlbetonbau. 115(10), 789-800. ISSN 0005-9900. doi:10.1002/best.202000020
LEUTBECHER, T.; RIEDEL, P., 2020. Compressive strength classes and performance classes of ultra-high-performance concrete (Part 2) | Druckfestigkeits- und Leistungsklassen für ultrahochfesten Beton (Teil 2). Betonwerk und Fertigteil-Technik/Concrete Plant and Precast Technology. 86(10), 46-53. ISSN 0373-4331
LEUTBECHER, T.; RIEDEL, P., 2020. Compressive strength classes and performance classes of ultra-high-performance concrete (Part 1) | Druckfestigkeits- und Leistungsklassen für ultrahochfesten Beton (Teil 1). Betonwerk und Fertigteil-Technik/Concrete Plant and Precast Technology. 86(9), 46-54. ISSN 0373-4331
